Keyah Math Module 9, Level 3
Mathematical Content: Basic algebra, formulae for gravitational attraction
 Determining the Mass and Density of the Earth:
Determining the Mass and Density of the Earth:
The goal of this study is to learn how the famous physicist, Sir Isaac Newton, computed the mass of the Earth, and then use this to compute its density.
Basic Concepts:
* Any object in the Universe attracts any other object.
* The force that moves objects toward each other is called gravity.
* The mass of an object is a fundamental property of the object with measured in kilograms (kg).
* Even though we often use weight and mass interchangeably in everyday language, the weight of an object depends on the force of gravity. If you went to the moon, your mass would not change but your weight would be much less. The weight of an object is the force of gravity on the object; this can be described by the equation
w = mg where m is the mass of the object and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
* The density of an object is the mass per unit volume.
In the year 1680, Sir Isaac Newton discovered the famous equation known as the Law of Gravitational Attraction on two objects. You will use this result, together with another result also due to Newton, to compute the mass of the Earth.

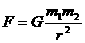 , describes the force with which two objects attract each other.
, describes the force with which two objects attract each other. 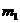 and
and 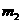 denote the masses of the two objects
denote the masses of the two objects 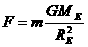
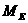 is the mass of the earth and
is the mass of the earth and 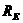 is the radius of the earth.
is the radius of the earth. 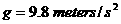 and we have
and we have 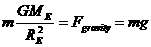 ,
, 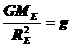 .
.
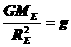 to estimate the mass, volume and density of the earth.
to estimate the mass, volume and density of the earth.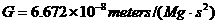
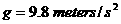
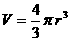
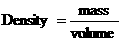
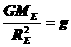 .
.